Как создать новый проект в pycharm
Как создать новый проект в pycharm
Create a Python project
Pure Python projects are intended for Python programming. A project helps you organize your source code, tests, libraries that you use, and your personal settings in a single unit. In case, you don’t need a project, you can edit your file in the LightEdit mode.
To create a project, do one of the following:
From the main menu, choose File | New Project
On the Welcome screen, click New Project
New Project dialog opens.
In the New Project dialog, specify the project name and its location. The dialog may differ depending on the PyCharm edition.
Next, click 
The following steps depend on your choice:
Next, specify the Location and Base interpreter of the new virtual environment.
Select the Make available to all projects checkbox if you want to reuse this environment when creating Python interpreters in PyCharm.
Specify a path to the Python executable (in case of non-standard installation)
Download and install the latest Python versions from python.org
Install Python using the Command-Line Developer Tools (macOS only).
Previously configured interpreter : if this option has been selected, choose the desired interpreter from the list, or (if the desired interpreter is not found), click Add Interpreter and choose the interpreter. See Configure a Python interpreter for details.
When PyCharm stops supporting any of the outdated Python versions, the corresponding Python interpreter is marked as unsupported.
Create a main.py welcome script : keep this option selected if you want PyCharm to add the main.py file to your project. This file contains a very simple Python code sample and can be a starting point of your project.
Once you created a project, you can proceed with configuring the project structure.
See more details on creating projects in PyCharm in the video tutorial:
Step 1. Create and run your first Python project
Before you start
Ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
You are working with PyCharm Community or Professional
You have installed Python itself. If you’re using macOS or Linux, your computer already has Python installed. You can get Python from python.org.
To get started with PyCharm, let’s write a Python script.
Create a Python project
Although you can create projects of various types in PyCharm, in this tutorial let’s create a simple Pure Python project. This template will create an empty project.
Choose the project location. Click 
Also, deselect the Create a main.py welcome script checkbox because you will create a new Python file for this tutorial.
Python best practice is to create a virtualenv for each project. In most cases, PyCharm create a new virtual environment automatically and you don’t need to configure anything. Still, you can preview and modify the venv options. Expand the Python Interpreter: New Virtualenv Environment node and select a tool used to create a new virtual environment. Let’s choose Virtualenv tool, and specify the location of the environment and the base Python interpreter used for the new virtual environment.
Specify a path to the Python executable (in case of non-standard installation)
Download and install the latest Python versions from python.org
Install Python using the Command-Line Developer Tools (macOS only).
Now click the Create button at the bottom of the New Project dialog.
Create a Python file
Select the option Python File from the context menu, and then type the new filename.
PyCharm creates a new Python file and opens it for editing.
Edit Python code
Let’s start editing the Python file you’ve just created.
Start with declaring a class. Immediately as you start typing, PyCharm suggests how to complete your line:
PyCharm informs you about the missing colon, then expected indentation:
Note that PyCharm analyses your code on-the-fly, the results are immediately shown in the inspection indicator in the upper-right corner of the editor. This inspection indication works like a traffic light: when it is green, everything is OK, and you can go on with your code; a yellow light means some minor problems that however will not affect compilation; but when the light is red, it means that you have some serious errors. Click it to preview the details in the Problems tool window.
If you notice any inspection warnings as you’re editing your code, click the bulb symbol to preview the list of possible fixes and recommended actions:
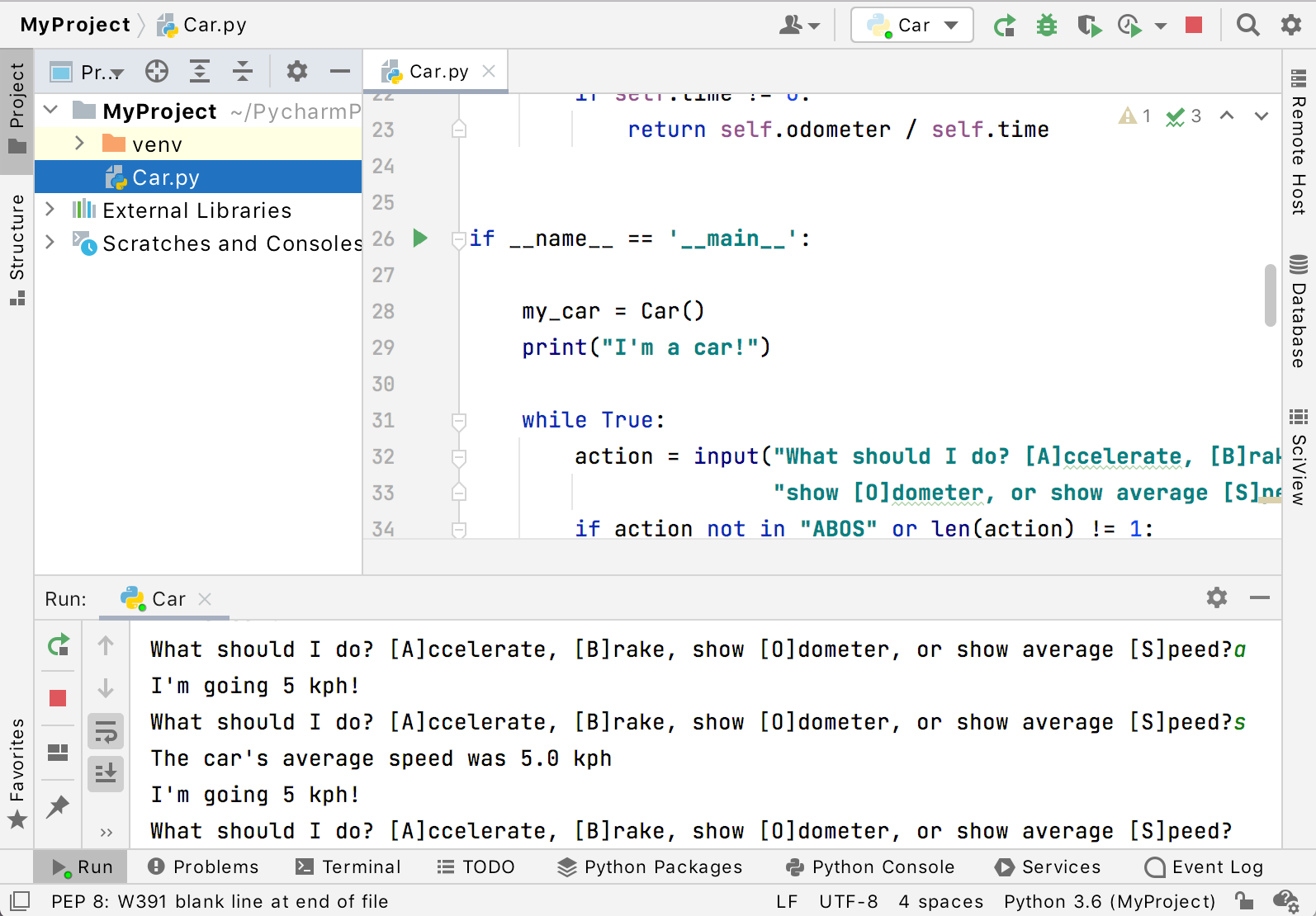
Let’s copy and paste the entire code sample. Click the copy button in the upper-right corner of the code block here in the help page, then paste it into the PyCharm editor replacing the content of the Car.py file:
This application is intended for Python 3
At this point, you’re ready to run your first Python application in PyCharm.
Run your application
Use either of the following ways to run your code:
If you click this icon, you’ll see the popup menu of the available commands. Choose Run ‘Car’ :
PyCharm executes your code in the Run tool window.
Here you can enter the expected values and preview the script output.
Note that PyCharm has created a temporary run/debug configuration for the Car file.
The run/debug configuration defines the way PyCharm executes your code. You can save it to make it a permanent configuration or modify its parameters. See Run/debug configurations for more details about running Python code.
Summary
Congratulations on completing your first script in PyCharm! Let’s repeat what you’ve done with the help of PyCharm:
Создание и настройка проекта в IDE PyCharm под Windows
Скачиваем и устанавливаем интерпретатор Python. Выбор версии за вами, но советую прочитать эту статью
Так как в 2020 году поддержка Python2 прекращается, устанавливаем Python3 с официального сайта
2. Выбор IDE
Лучшей средой разработки является PyCharm от гениальных JetBrains.
Устанавливаем PyCharm. У кого нет лицензии — скачивайте Community Edition.
3. Создание проекта
Нажимаем «Create New Project»
Выходит окно с параметрами проекта, где следует задать путь расположения проекта и выбрать интерпретатор.
Скрипт создается так:
4. Создаем виртуальное окружение
При работе с несколькими проектами хорошо иметь виртуальное окружение. Подробнее про него можно прочитать в этой статье:
Заходим в раздел File->Settings
Далее Project: Название вашего проекта->Project Interpreter

Здесь вы можете подключить модули(необходимо нажать зеленый плюс) и создать виртуальное окружение(нажмите на шестеренку)
Дальше Create VirtualEnv
Задаем параметры виртуального окружения (имя и интерпретатор)
И видим, что виртуальное окружение создано и готово к работе.
Можно начинать писать код.
Добавить комментарий Отменить ответ
Для отправки комментария вам необходимо авторизоваться.
Generating a Project from a Framework Template
PyCharm can create new framework-specific applications for you, set up their structure, and download the required packages, if necessary. You can also use the Yeoman generator, see Yeoman for details.
AngularJS application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane, specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
Learn more about installing dependencies in the Install Dependencies section of the readme.md file.
HTML5 Boilerplate, Web Starter Kit, Bootstrap, or Foundation application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the left-hand pane, choose the template to use depending on your preferences and the functionality to be implemented in your application:
HTML5 Boilerplate: select this option to use the HTML5 Boilerplate template. This is a starting project template that can be easily adapted to your needs.
Web Starter Kit: select this option to use the Web Starter Kit.
Bootstrap: select this option to use the Bootstrap template, which is an elaborate modular toolkit with rich HTML, CSS, and JavaScript support.
Foundation: select this option to use the Foundation framework.
The set of controls in the right-hand pane depends on the chosen template.
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
Express application
To generate a Node.js application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane:
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
The Express template engine to use. From the Template engine list, choose one of the following:
The CSS engine to use. From the CSS engine list, choose one of the following:
PyCharm launches the Express Project Generator tool that downloads all the required data, sets up the project structure, and opens the project either in the current window or in a new one, depending on your choice.
Meteor application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane:
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
Specify the location of the Meteor executable file (see Installing Meteor).
From the Template list, choose the sample to generate. To have a basic project structure generated, choose the Default option.
PhoneGap or Cordova application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane:
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
React application with create-react-app
Learn more about installing React and creating React applications from the React official website.
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane, specify the project folder, the Node.js interpreter to use, and the path to the create-react-app package.
Vue.js application with @vue/cli
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the right-hand pane:
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
In the Node Interpreter field, specify the Node.js interpreter to use. Select a configured interpreter from the list or choose Add to configure a new one.
Step 4. Create and Run your first Django project
Before you start
Make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
You are working with PyCharm version 2016.1 or later. If you still do not have PyCharm, download it from this page. To install PyCharm, follow the instructions, depending on your platform.
You have at least one Python interpreter properly installed on your computer. You can download an interpreter from this page.
You have Django package installed. To learn how to install packages using the PyCharm UI, read the section Install, uninstall, and upgrade packages. You can also install Django as described in the page How to install Django.
This tutorial has been created with the following assumptions:
Django 1.x (higher than Django 1.10).
The example used in this tutorial is similar to the one used in Django documentation. Sample project can be downloaded from here.
Creating a new project
Actually, all new projects are created same way: by clicking the New Project button in the Quick Start area of the Welcome screen:
If you have an already opened project, create a new one by choosing File | New Project. from the main menu.
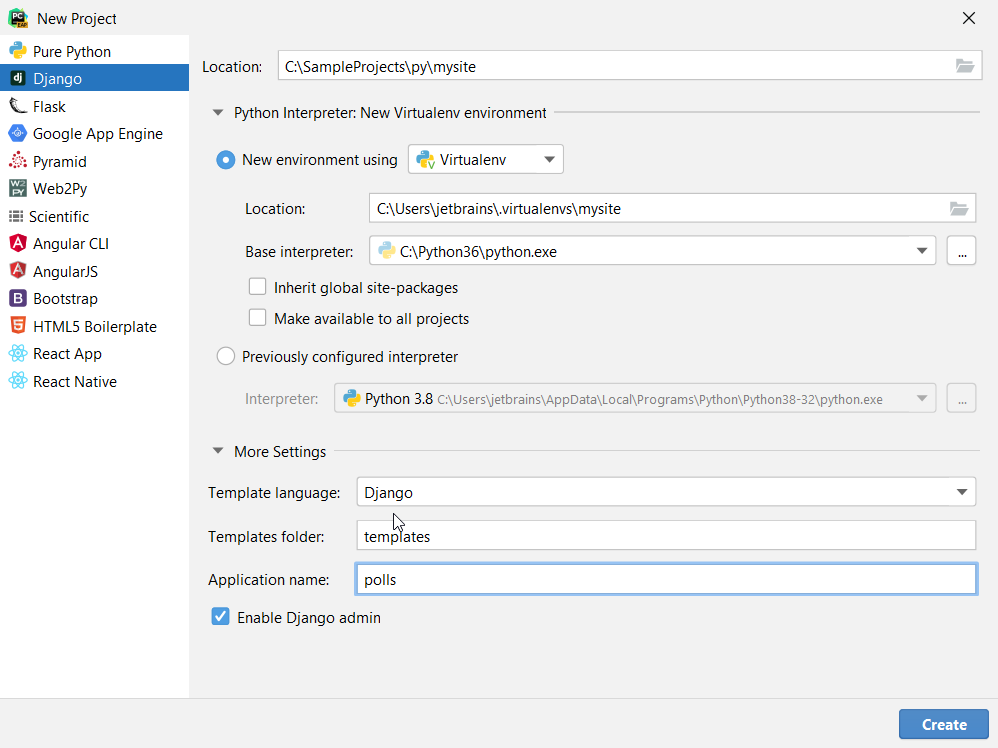
Then, select the desired project type (here it is Django). Specify the project name and location.
Python best practice is to create a virtualenv for each project. In most cases, PyCharm create a new virtual environment automatically and you don’t need to configure anything. Still, you can preview and modify the venv options. Expand the Python Interpreter: New Virtualenv Environment node and select a tool used to create a new virtual environment. Let’s choose Virtualenv tool, and specify the location of the environment and the base Python interpreter used for the new virtual environment.
Next, expand the More Settings node and specify the Django-related settings. In the Application name field specify the application name (here it is polls ).
Exploring project structure
As mentioned above, basically, the stub project is ready. It contains framework-specific files and directories. Same happens when you create a project of any supported type, be it Pyramid, or Google App Engine.
Let’s see how the structure of the new project is visible in the Project tool window.
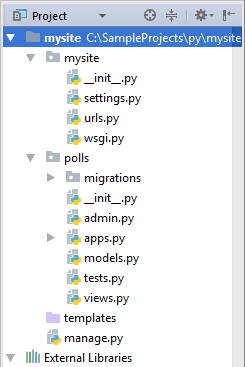
Project view of the Project tool window
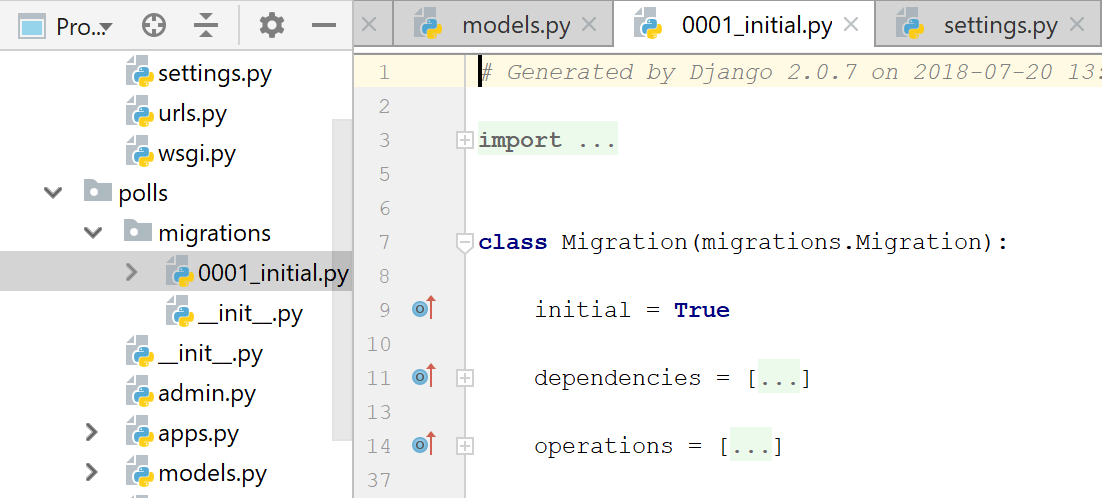
This view is displayed by default. It shows the Django-specific project structure: polls and mysite directories; also, you see the manage.py and settings.py files.
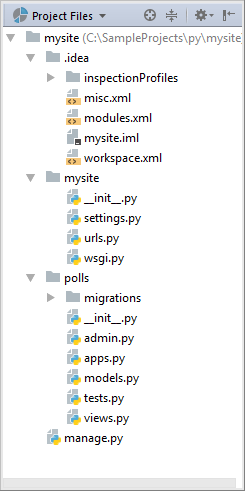
Project Files view of the Project tool window
Let’s return to the Project view.
What do we see in the Project view?
mysite directory is a container for your project. In the Project view it is denoted with bold font.
manage.py : This is a command-line utility that lets you interact with your Django project. Refer to the Django documentation for details.
The nested directory mysite is the actual Python package for your project.
mysite/__init__.py : This empty file tells Python that this directory should be considered a Python package.
mysite/wsgi.py : This file defines an entry-point for WSGI-compatible web servers to serve your project. See How to deploy with WSGI for more details.
The nested directory polls contains all the files required for developing a Django application (at this moment, these files are empty):
Again, polls/_init_.py tells Python that this directory should be considered a Python package.
polls/models.py : In this file, we’ll create models for our application.
polls/views.py : In this file, we’ll create views.
templates directory is by now empty. It should contain the template files.
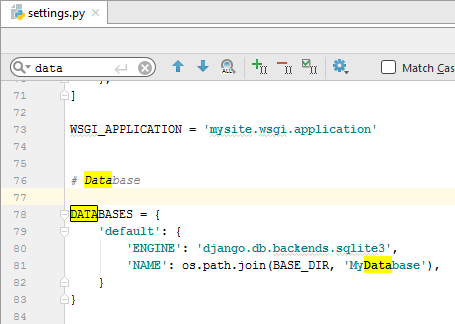
Configuring the database
In the ‘NAME’ line, enter the name of the desired database, even though it doesn’t yet exist.
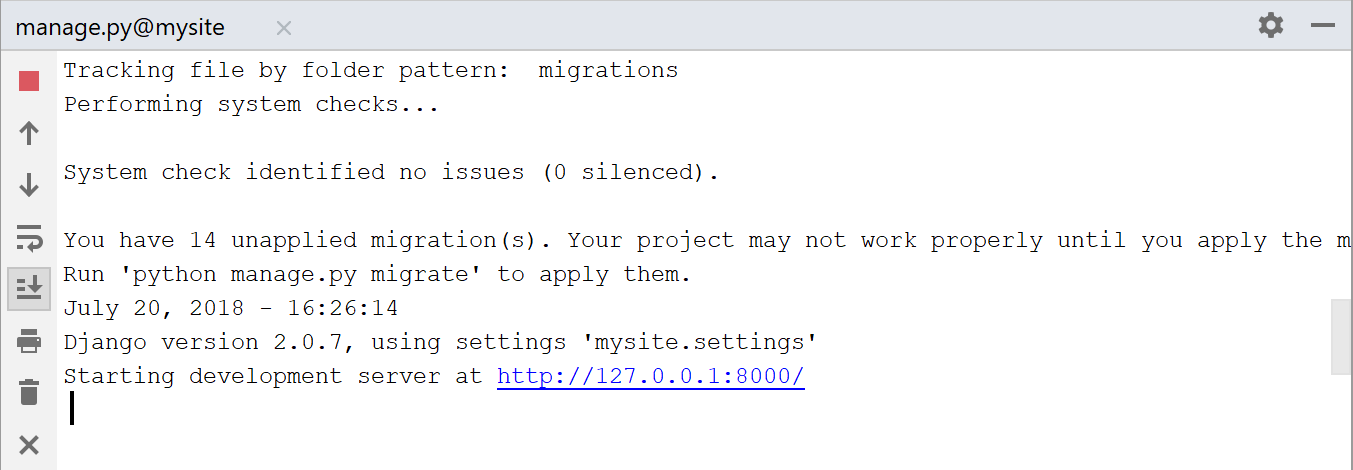
Launching Django server
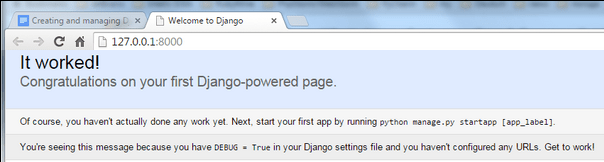
Follow the suggested link and see the following page:
Creating models
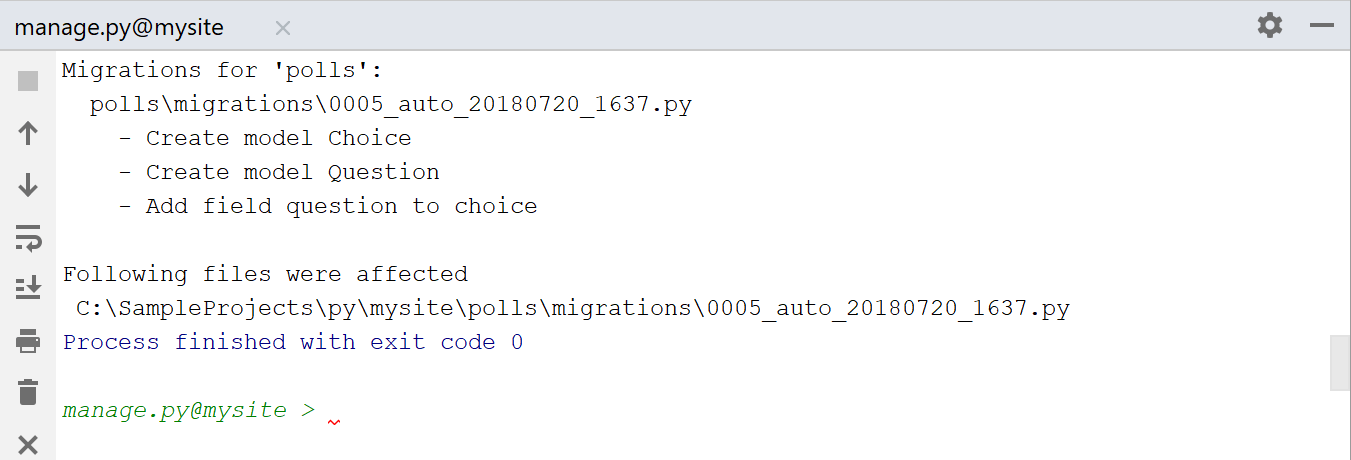
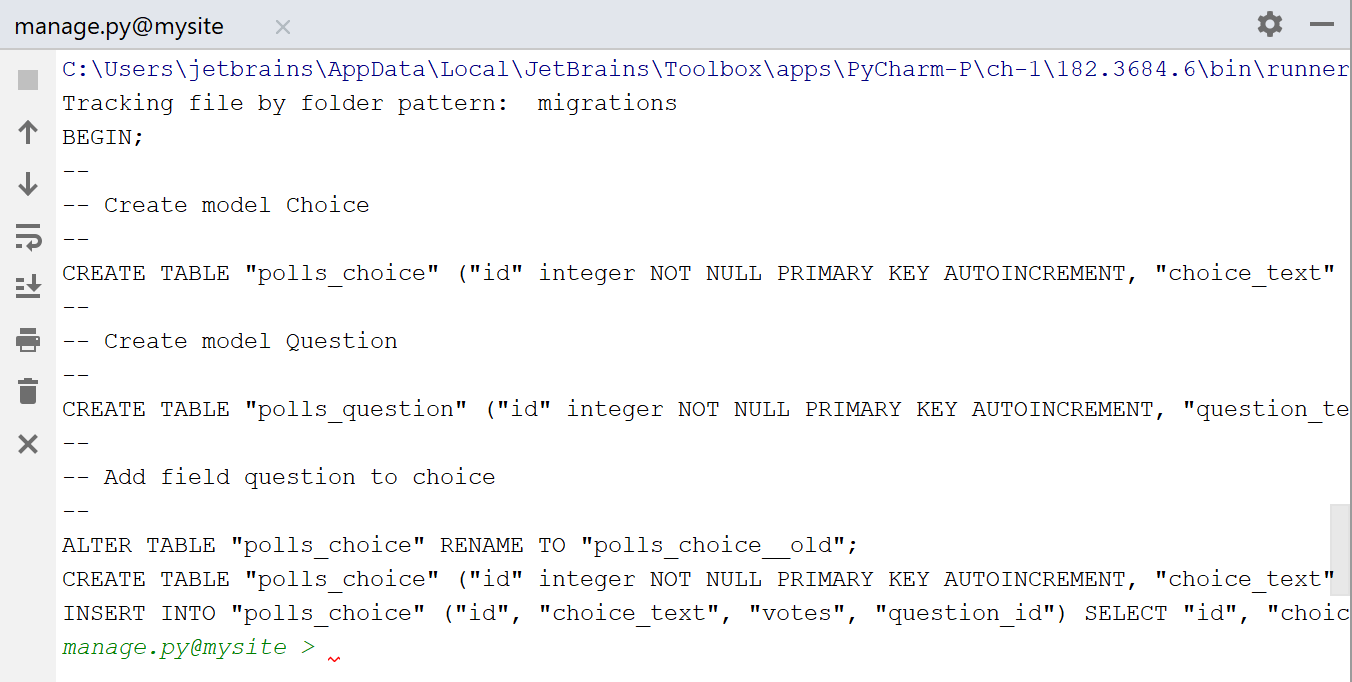
Creating database
We have to create tables for the new model. For this purpose, we’ll use the magic Ctrl+Alt+R shortcut to invoke the manage.py console. First command to perform is makemigrations polls :
Next, after the prompt, type the following command:
sqlmigrate polls 0001
Finally, run migrate command to actually create these tables in your database:
Performing administrative functions
First thing, create a superuser. To do that, type the createsuperuser command in the manage.py console, specify your email address, and password:
Open the admin.py file in the polls directory for editing, and see the following code that already exists:
However, we need to enable editing functionality for the admin site.
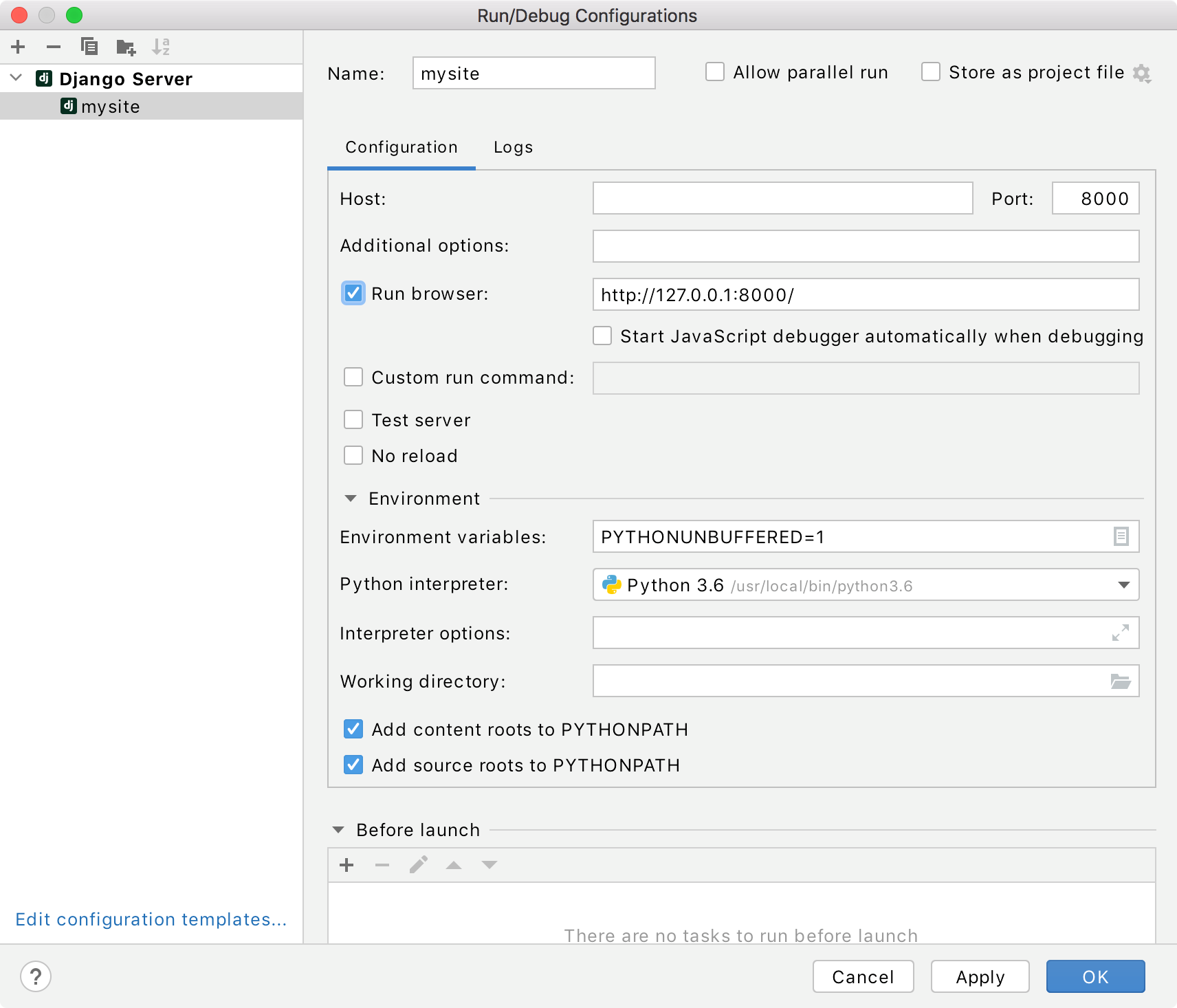
Preparing run/debug configuration
We are now ready to go to the admin page. Sure, it is quite possible to run the Django server, then go to your browser, and type the entire URL in the address bar, but with PyCharm there is an easier way: use the pre-configured Django server run configuration with some slight modifications.
Do not set up a working directory for the default Run/Debug Configurations listed under the Templates node. This may lead to unresolved targets in newly created Run/Debug Configurations.
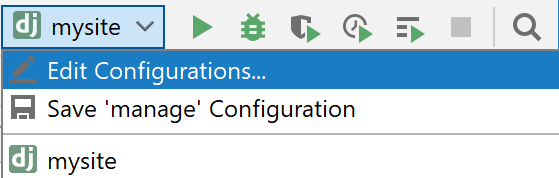
To open this run/debug configuration for editing, on the main toolbar, click the run/debug configurations selector, and then select Edit Configurations (or select Run | Edit Configurations from the main menu):
In the Run/Debug Configuration dialog, give this run/debug configuration a name (here it is mysite ), enable running the application in the default browser (select the checkbox Run browser ) and specify the page of the site to be opened by default (here this page is http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/ ):
Launching the admin site
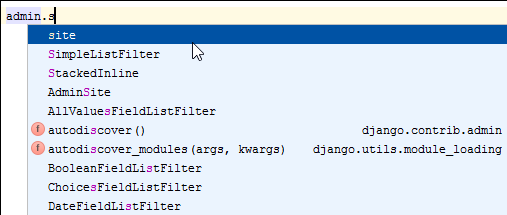
We must tell admin that Question objects have an admin interface; to do that, let’s open the file polls/admin.py for editing (select it in Project view and press F4 ), and type the following code:
Again pay attention to the code completion:
Refresh the page and see that Polls section with Questions appeared:
Click Add to create some questions.
Editing admin.py
However, each question has a number of choices, but choices are still not available. Again, open for editing the file polls/admin.py and change it as follows:
Now look at the Change question page:
Writing views
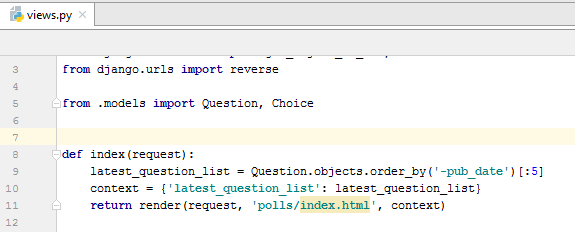
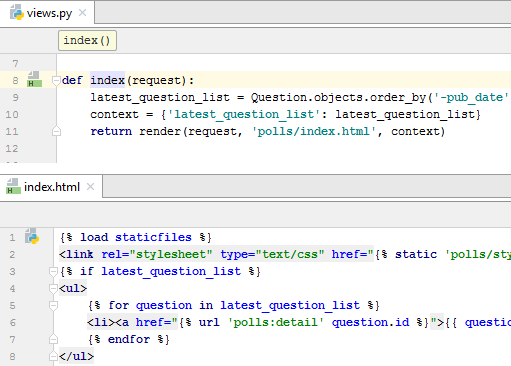
Open the file polls/views.py for editing and type the following Python code:
Next, add a new file to the polls directory with the name urls.py and type the following code in it:
Next, open for editing the file mysite/urls.py (which PyCharm has already created for you) and add a URL for the index page. You should end up with the following code:
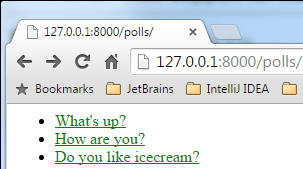
Now, open the page 127.0.0.1:8000/polls/ and enjoy:
Next, let’s add more views. Again, add the following code to the file polls/views.py :
Wire these new views into the polls.urls module by adding the following url() calls :
If you now open the corresponding pages in your browser, you will see, for example:
Creating Django templates
Open for editing the file polls/views.py and replace its contents with the following code:
By the way, pay attention to the import assistant that helps you create import statements.
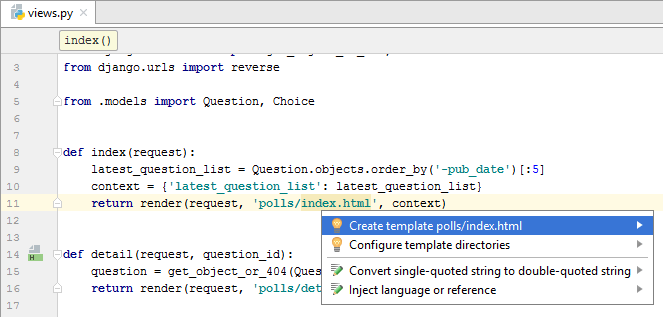
The first thing you notice is an unresolved reference to the page index.html :
By now, the file index.html is empty. Add the following code to it:
No polls are available.
For Django 3 and later, you need to use <% load static %>instead <% load staticfiles %>.
Pay attention to the icons 

These icons enable you to jump between a view method and its template straight away. Read more about this kind of navigation in the articles Navigate between templates and views and Part 6. Django-specific navigation.
Using a Style Sheet
Resolve this reference in the following way:
Provide some contents to the created Style Sheet, depending on your preferences. For example, we’d like to see a bulleted list of questions colored green:
Here we are!
Test it…
Now let’s see how PyCharm helps simplify testing your application.
There is already the file tests.py in the polls directory. By now, this file is empty. Naturally, it is advisable to place the new tests in this particular file. For example, we’d like to make sure our poll is not empty:
The test results show in the Test Runner tab of the Run tool window:
Summary
This brief tutorial is over. You have successfully created and launched a simple Django application. Let’s repeat what has been done with the help of PyCharm:
A Django project and application have been created
Getting started with PyCharm
In the previous two posts of this absolute beginner series, we installed Anaconda Navigator and learned about virtual environments. Having completed the basic setup, it’s now time to choose an IDE and get to coding.
I should mention from the start that choosing and IDE is not crucial when starting learning. Just go with anything that is comfortable for you… Any recommendations in this post are my preferences which might not match yours. That is absolutely fine, all is subjective 🙂
PyCharm Installation and Setup
PyCharm is developed by JetBrains which produces IDE applications for many popular languages (Javascript, C/C++, PHP, Ruby etc.). I’ve worked with PHPStorm for several years before starting with Python, so my transition to PyCharm was quite smooth.
PyCharm is available for download on Windows, Mac and Linux. The Professional Edition trial is 30 days, but, unlike other of their IDEs, JetBrains offers a perpetually free Community Edition.
Download and installation is a straightforward process. When launching PyCharm for the first time, you’ll have to go through a couple of settings. Choose a dark or light theme (I chose the dark side if anyone wonders 😄 ) and skip installation of other plugins for now. As a side note, you might notice that one of the plugins is for supporting the R language which was mentioned as an alternative to Python.
After setup is complete, you’ll see the welcome screen. It’s time to create our first project in PyCharm.
Creating a Project
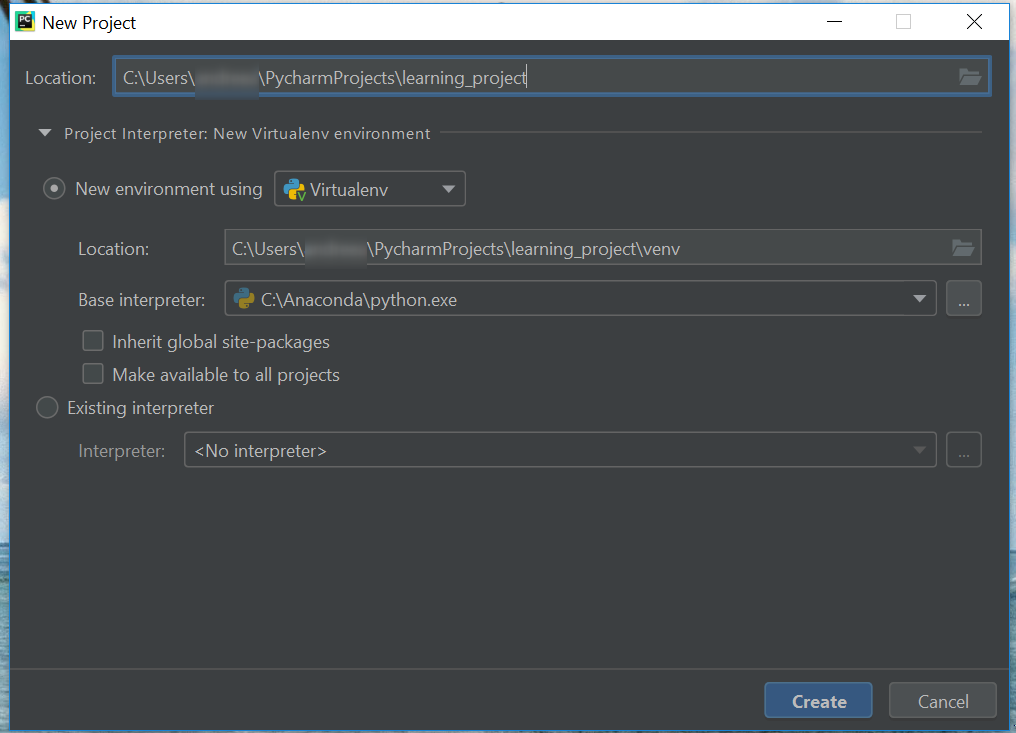
On the Welcome screen, simply click Create a Project.
I’ve named the project learning_project. It will have its own folder on the disk. I’ve left the default path, but you can place the project wherever you wish.
Expanding Project Interpreter: New Virtualenv environment we can see more details about the project.
Most important, PyCharm will create a new virtual environment for this project. This is done for all new projects, without any additional settings having to be made. Quite handy…
Then we see the base interpreter is the python we installed with Anaconda. So PyCharm recognizes any existing Python installations.
The other 2 checkbox options are more advanced, so there’s no need to worry about them for now.
Creating a Python file and running it
On the left side of the UI we see the Project. Right click on its name and create a new Python file.
In the Python file add the same code from the numpy test in the previous post:
To run the file, press CTRL+SHIFT+F10 (or just SHIFT+F10, depending on version). You’ll see the following error: No module named ‘numpy’
Do you have any idea what the problem is?
Well, we haven’t installed numpy inside this project’s virtual environment.
Installing a Package in PyCharm
Packages in PyCharm can be installed using pip, the package installation manager for Python.
In the lowest bar of the UI, click on terminal and type
pip will then download and install the package inside the virtual environment. Any dependencies will automatically be collected and installed as well.
When the installation is successfully complete, you should see the following:
Running the file again will prove successful this time, with the expected value [1, 2, 3] being displayed on the screen.
Having a virtual environment automatically created for every project is just one of PyCharm’s features. The Getting started guide on the official site provides more thorough introduction.
Alternatives to PyCharm
There are of course many alternatives to PyCharm, which proves Python is a very popular language. Two are available inside Anaconda Navigator: Spyder and Visual Studio Code.
Spyder is a Python IDE aimed specifically at Data Scientists. You can check out a great overview video here.
Visual Studio Code
A lightweight free code editor from Microsoft, Visual Studio Code is available on all platforms. It’s not set up for Python out of the box, but it has official Python support via an extension. Check out the get started guide.
Like Visual Studio Code, Atom is a light editor, not specific to Python, but highly configurable and offering Python support via extensions.
If you want to read more, here is a great overview of IDEs and code editors for Python: https://realpython.com/python-ides-code-editors-guide/
Conclusion
You can check them all out before deciding which one to use. My advice is not to dwell too much on this now, any option is good enough to start learning about Python, Machine Learning or Data Science… and you can always switch IDEs when you are more experienced.
Next post will be an overview of Jupyter Notebooks, an indispensable tool for any Python user.
Your opinions, feedback or (constructive) criticism are welcomed in discussions below or at @mariussafta
Join our Facebook and Meetup groups and keep an eye out for discussions and future meetups.
Был задан вопрос: Что такое PyCharm?
Компания русских программистов, проживающих по большей части в Праге, JetBrains любезно предоставила нам лицензии на использование всех своих продуктов в версиях Proffessional. Грех этим не воспользоваться. В рамках курса «Программирования» нам интересен PyCharm — IDE для Python. Вот вам несколько уроков для ответа на вопрос в заголовке:
Короткий вводный урок по PyCharm
Общая информация
PyCharm – это интеллектуальная Python IDE с полным набором средств для эффективной разработки на языке Python. Выпускается в двух вариантах – бесплатная версия PyCharm Community Edition и поддерживающая больший набор возможностей PyCharm Professional Edition. PyCharm выполняет инспекцию кода на лету, автодополнение, в том числе основываясь на информации, полученной во время исполнения кода, навигацию по коду, обеспечивает множество рефакторингов.
Основные отличия Community Edition и Professional Edition
Comunity edition:
Professional Edition:
Напоминаю, компания Jetbrains любезно предоставила студентам Бизнес-информатики лицензии на все свои продукты в версии Professional до января 2020 года. Лицензии в индивидуальном порядке можно получить в ауд. 115/3б и чем раньше, тем лучше.
Ключевые возможности
Лицензирование
PyCharm Professional Edition имеет несколько вариантов лицензий, которые отличаются функциональностью, стоимостью и условиями использования. Является бесплатным для образовательных учреждений и проектов с открытым исходным кодом.
PyCharm Community Edition — бесплатная версия, обладающая усеченным набором возможностей. Распространяется под лицензией Apache 2.
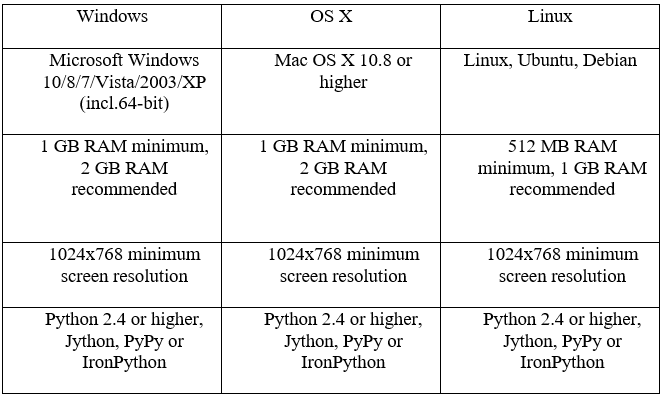
Системные требования
Создание и настройка проекта
Все процессы описаны для версии PyCharm Professional 2016.1.4.
Для создания нового проекта в меню File необходимо выбрать пункт New Project.
В появившемся окне указываем параметры создаваемого проекта. В поле Location можно указать путь, по которому будет храниться создаваемый проект. В поле Interpreter выбираем версию Python под которой необходимо создать проект. В данном примере выбрана версия Python 2.7.
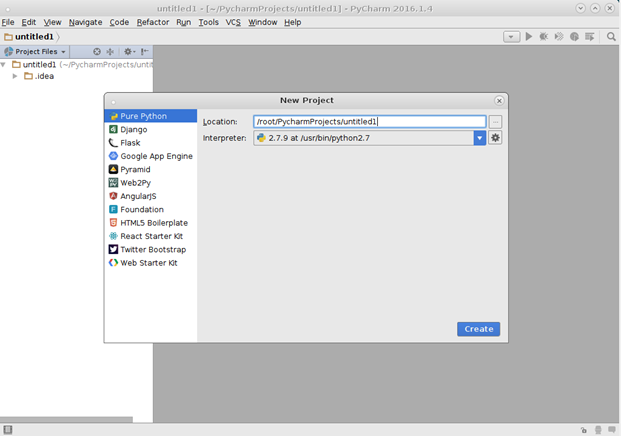
Для завершения создания проекта нажать кнопку Create.
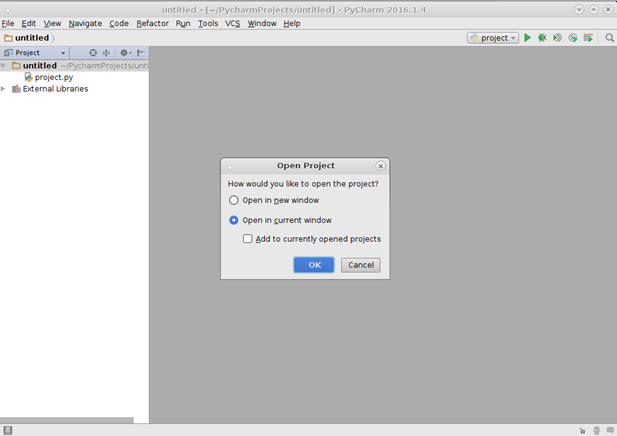
В данном окне можно выбрать, как создастся новый проект — в новом окне или в текущем.
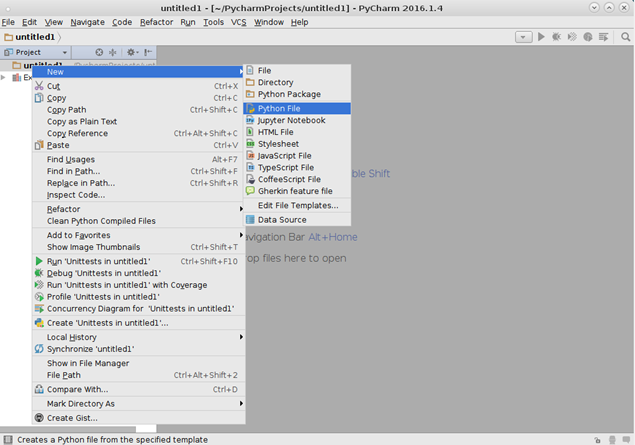
Проект создан, можно начинать писать код. Для этого нужно создать файл с расширением Py. Правая кнопка мыши – New – Python File.
Задаем название для нового файла, нажимаем ОК. В названии можно использовать буквы латинского алфавита и цифры. Расширение указывать не нужно, оно указано в поле под именем файла.
Проект создан, можно писать код программы. Также в проект можно добавить уже существующие файлы с кодом. Для этого можно просто перенести необходимый файл в каталог проекта. После чего он сразу отобразится в файлах проекта.
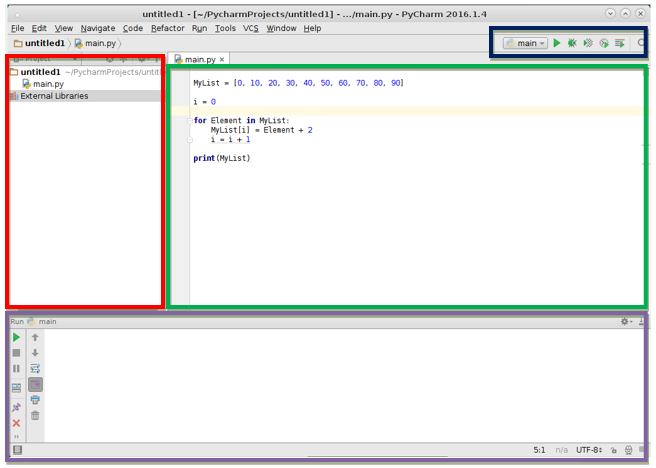
Интерфейс и выполнение проекта
Окно программы можно разделить на 4 области. В красной отображаются файлы проекта. В зеленой происходит непосредственная работа с файлами, в том числе — пишется код. Синяя служит для быстрого доступа к функциям построения, запуска и отладки проекта. Дополнительно присутствует функция поиска по коду. Фиолетовая область – консоль вывода.
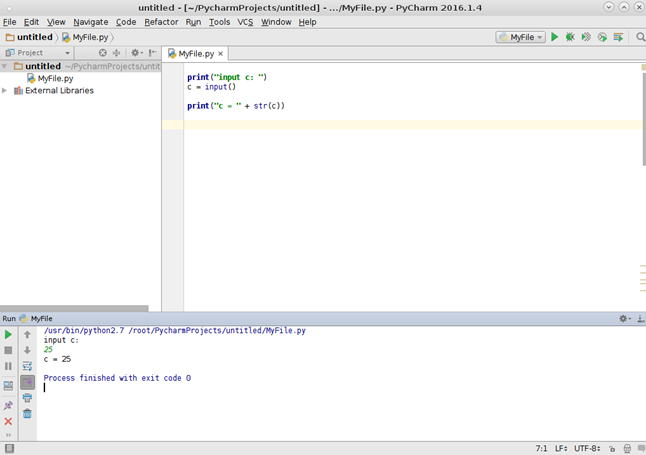
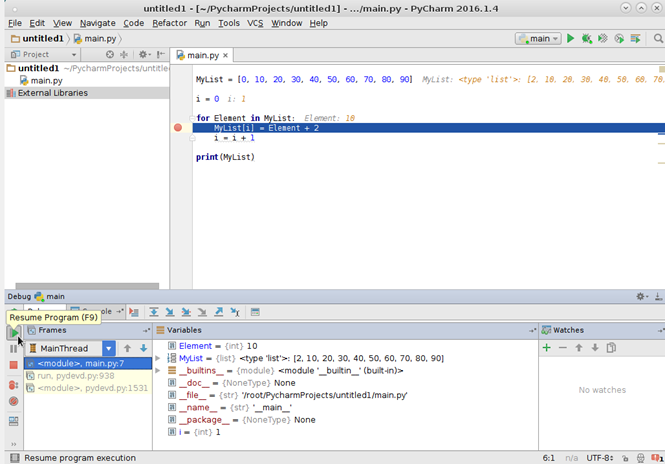
Приведена программа, которая увеличивает значения массива на 2.
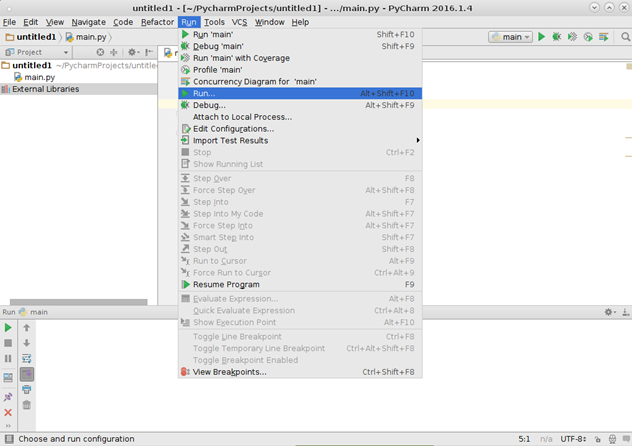
Чтобы выполнить проект, в меню Run необходимо выбрать пункт Run или воспользоваться сочетанием клавиш Alt+Shift+F10.
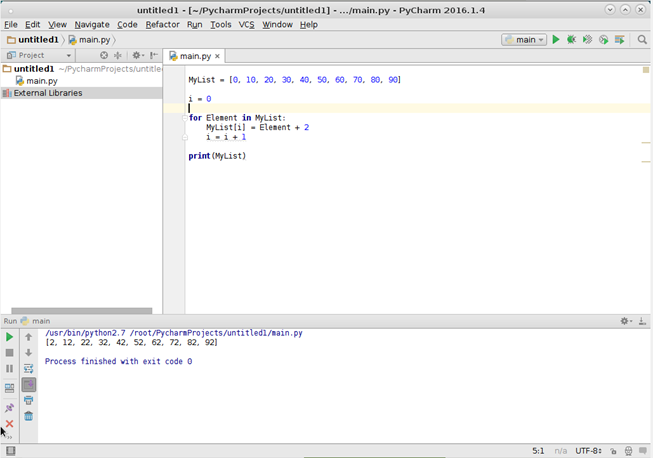
После выполнения результат можно увидеть на вкладке вывода.
Если код программы предусматривает пользовательский ввод, то консоль вывода может служить консолью ввода данных.
Результат работы программы.
Отладка проекта
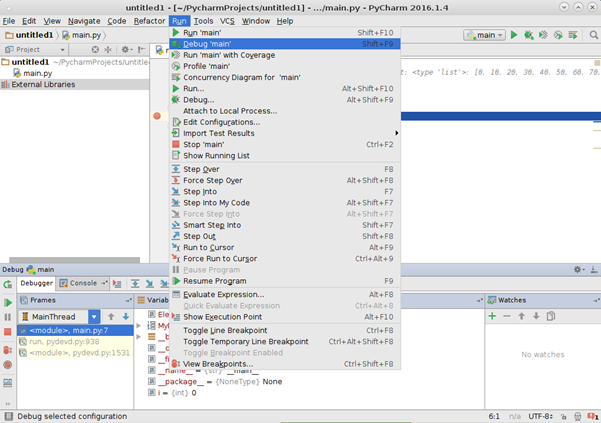
Для отладки своего приложения можно пользоваться «брейкпоинтами» (преднамеренное прерывание выполнения программы). Для того чтобы поставить breakpoint нужно нажать левую кнопку мыши слева от строки кода, на которой нужно остановить программу.
После чего выбрать пункт Debug в окне Run проект.
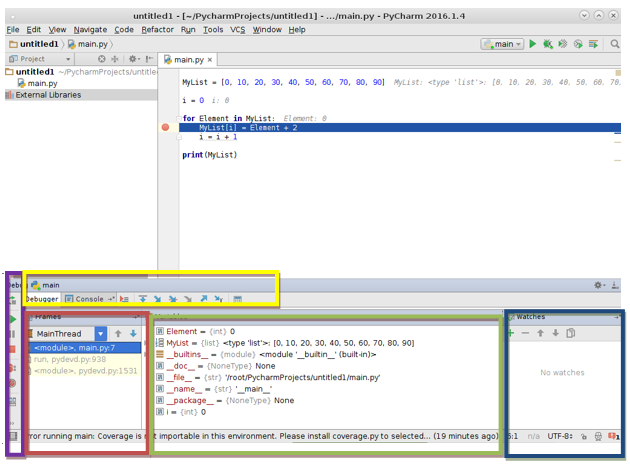
Программа остановит свое выполнение на указаном месте, после чего на вкладке Debugger в области Variables(зеленая область на рисунке) можно отслеживать знаечния всех переменных. Также значения перемнных можно увидеть непосредственно в окне с кодом программы.
Фиолетовая область служит для быстрого доступа к необходимым функциям при отладке(от верхней к нижней кнопки): перезапуск проекта, выполнить программу до следующей точки прерывания, пауза(не активна в данный момент), принудительное завершение программы, просмотр выставленных «брейкпоинтов», игнорировать «брейкпоинты»(программа будет выполняться до конца).
Желтая область служит для переключения между вкладками дебагера и консолью вывода, также в ней находятся кнопки для отладки: шаг с заходом, шаг с обходом, шаг с выходом.
Панель Frames (красная область) позволяет получить доступ к списку потоков вашего приложения. Для каждого потока, вы можете просматривать структуру стека, изучить кадры, перемещаться между кадрами, и автоматически переходить к исходному коду в редакторе.
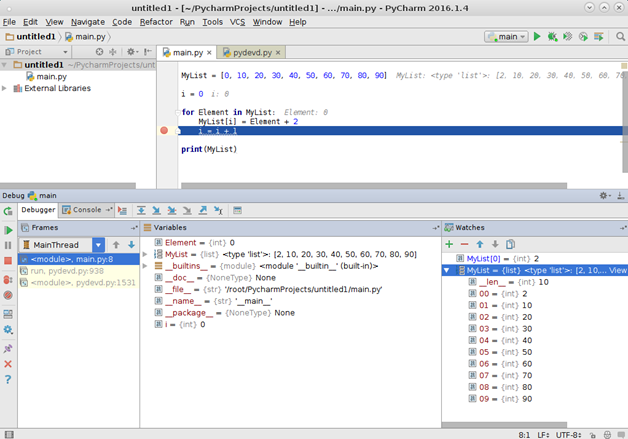
Если нужно отследить значение определенной переменной, можно воспользоваться окном Watches. Чтобы добавить интересующую Вас переменную необходимо нажать на зеленый плюс и вписать название переменной из кода программы.
Аналогично можно добавить любую другую переменную. Например, чтобы добавить массив, так же нужно указать его имя, после чего во вкладке watches появятся значения элементов массива.
Контроль значения переменной:
Контроль значений всего массива:
Для перехода к следующему шагу программы можно нажать кнопку Resume program или воспользоваться клавишей F9.
Таким образом, можно контролировать ход выполнения программы. Если значение переменной больше отслеживать не требуется, то можно удалить ее из списка переменных. Для удаления используется значок красного минуса.
Creating a Flask Project
Flask project in intended for productive development of the Flask applications. PyCharm takes care of creating the specific directory structure, and settings.
To create a Flask project, follow these steps
In the New Project dialog, do the following:
Specify project location.
Next, click 
The following steps depend on your choice:
Next, specify the Location and Base interpreter of the new virtual environment.
Select the Make available to all projects checkbox if you want to reuse this environment when creating Python interpreters in PyCharm.
Specify a path to the Python executable (in case of non-standard installation)
Download and install the latest Python versions from python.org
Install Python using the Command-Line Developer Tools (macOS only).
Previously configured interpreter : if this option has been selected, choose the desired interpreter from the list, or (if the desired interpreter is not found), click Add Interpreter and choose the interpreter. See Configure a Python interpreter for details.
When PyCharm stops supporting any of the outdated Python versions, the corresponding Python interpreter is marked as unsupported.
Click 
From the Template language list, select the language to be used.
In the Templates folder field, specify the directory where the templates will be stored, and where they will be loaded from. You can specify the name of the directory that doesn’t yet exist; in this case, the directory will be created.
You can run the created application by pressing Shift+F10 Preview the run results.
Note that the application was run with the following Flask specific variables:
access_management – the module name
access – the target file in the module
For more information about the FLASK_APP variable, refer to Flask CLI documentation.
FLASK_ENV=development – Sets one of possible environments.
You can change Flask specific variables by editing the corresponding parameters of the Flask Server Run/Debug configuration.
Создание первого веб-приложения с помощью Django
Мотивация
Простая в использовании IDE (интегрированная среда разработки). На моей нынешней работе (системным инженером) мне пришлось разрабатывать сценарии для автоматизации создания документов. Одна из проблем конкретного набора инструментов, который мы используем, заключается в том, что в нем нет редактора исходного кода. Нет подсветки синтаксиса или завершения кода. Это очень неудобно. Я понятия не имею, работает ли то, что я пишу, пока не запущу это и не увижу ошибки / предупреждения.
Отладка выполняется с помощью операторов печати. Так работать нельзя.
Этот простой язык программирования может пригодиться мне в будущем. В наши дни освоить большинство языков программирования довольно просто. Я искал тот, который имел бы хорошую поддержку (документацию, сообщество пользователей, учебные пособия), требовал бы минимального кода для достижения необходимого результата и был легко читаем.
Бонусом, поскольку я не являюсь веб-разработчиком, работающим на полную ставку, является то, что я смог бы потенциально использовать его для других приложений.
Работает быстро, без кучи ерунды. Поскольку это побочный проект, который дополняет мою постоянную работу и обязанности в семье, я не хотел тратить многие часы на настройку. Я хотел быстро получить прототип, чтобы можно было приступить к реальной работе.
Победители…
Веб-фреймворк Django, использующий Python. Оказывается, этот инструмент автоматизации тестирования, который мы планировали использовать на работе, использует Python, так что это сыграло большую роль в том, что я обратил на него внимание, как на язык программирования общего назначения.
У меня был некоторый опыт работы с Java, но Spring оказался слишком тяжелым для этого проекта. Решения на основе Javascript, такие как стек MEAN, выглядели мощно, но я стараюсь не иметь с ними дел, если только это не (внешний интерфейс).
PyCharm. Выбрав Python, выбрать IDE было довольно просто. У PyCharm много фанатов, и я обнаружил, что к нему легко привыкнуть по сравнению с плагином PyDev в Eclipse или редактором IDLE, который поставляется вместе с Python.
Давайте создадим веб-приложение!
Внимание : все это я проделал на своем MacBook. Шаги будут отличаться, если вы используете Windows. Мой стационарный компьютер сейчас пылится и используется только эпизодически (для игр).
Установите Python
Создайте виртуальную среду
Предыдущее действие изолирует среду разработки и сохранит порядок на случай, если вы работаете над другими проектами, которые могут иметь другие зависимости.
Сначала создайте папку для проекта.
Затем создайте и активируйте виртуальную среду. Вы узнаете, что это работает, когда увидите «(myvenv)» в командной строке терминала.
Установите Django
Введите приведенную ниже строку, и веб-фреймворк Django будет установлен. Серьезно, это так просто.
Создайте проект Django
Создадим наш первый проект Django.
Это действие создает структуру каталогов, а также файлы, необходимые для начала работы. Это выглядит примерно так.
Настройте PyCharm для комфортной работы
Для работы с этими файлами можно использовать любой текстовый редактор, но мы не дикари. Пришло время установить PyCharm.
Перейдите на официальную страницу загрузки PyCharm и скачайте версию Community Edition. Это бесплатно, и мне нравится, что это бесплатно. Когда PyCharm будет установлен, откройте его, и вы увидите что-то вроде этого.
Откройте созданный вами проект Django
Нажмите кнопку « Открыть» и найдите каталог веб-приложения, который вы создали ранее.
Нажмите кнопку « Открыть», чтобы выбрать его в качестве рабочего каталога, после чего вы увидите структуру каталогов проекта.
Подготовьте сервер к работе
Проект уже должен быть направлен в интерпретатор Python в виртуальной среде, но на тот случай, если это еще не сделано, перейдите в PyCharm → Preferences, и убедитесь в том, что у вас заданы настройки, указанные ниже.
Следующим шагом является настройка конфигурации запуска / отладки. Для этого перейдите в Run → Edit Configurations.
Мы готовы к запуску
Если вы перейдете по ссылке, то увидите, как взлетает ракета. Наслаждайтесь тем, чего вы достигли.
Заключение
Еще очень много предстоит сделать, но выполнение всего этого менее чем за 15 минут является свидетельством того, как далеко продвинулись современные веб-технологии. Даже для такого отставшего любителя, как я, было легко и приятно вернуться в седло.
Пожалуйста, оставляйте ваши мнения по текущей теме материала. Мы очень благодарим вас за ваши комментарии, дизлайки, подписки, лайки, отклики!
Пожалуйста, оставляйте свои комментарии по текущей теме статьи. За комментарии, лайки, дизлайки, подписки, отклики низкий вам поклон!
Вадим Дворников автор-переводчик статьи « Creating My First Web App with Django »
Русские Блоги
Начало работы с PyCharm
Начало работы с PyCharm
Что содержит этот учебник
Целью этого учебника является пошаговое руководство по созданию, эксплуатации и отладке простых проектов Python с использованием PyCharm (Python IDE) и полного набора инструментов для эффективной разработки.
Ничего не участвует в этом уроке
Программирование на Python выходит за рамки этого руководства. Чтобы узнать больше о языке Python, см.Официальный сайт。
Прежде чем начать
Убедитесь в том, что:
Загрузите и установите PyCharm
Если у вас нет PyCharm, пожалуйста, перейдите сюдастраницаСкачать. Чтобы установить PyCharm, следуйте инструкциям, в зависимости от вашей платформы.
Запустить PyCharm
В зависимости от вашей операционной системы, есть много способов запустить IDE.
PyCharm запускает и отображаетЭкран приветствия:
Создайте простой проект Python в PyCharm
Чтобы создать новый проект, нажмите ссылку «Создать новый проект». Вы увидите диалоговое окно «Создать новый проект», в котором вы должны определить все необходимые настройки для нового проекта.
Далее выберите тип проекта. PyCharm предлагает несколько шаблонов проектов для разработки различных типов приложений (Django, Google AppEngine и т. Д.). Когда PyCharm создает новый проект из шаблона проекта, он генерирует соответствующую структуру каталогов и определенные файлы.
Наконец, давайте выберем интерпретатор Python. Как видите, PyCharm сообщает вам, что интерпретатор Python не был выбран. Поскольку вы можете использовать хотя бы один интерпретатор Python, мы определим его как интерпретатор проекта.
После того, как все необходимые настройки будут выполнены, кнопка OK станет активной, поэтому щелкните ее, чтобы подготовить проект.
Изучите и настройте структуру проекта
Вы можетеОкно инструмента проектаПосмотреть исходную структуру проекта:
Как видите, проект содержит только корневой каталог проекта и интерпретатор Python, указанный в узле «Внешние библиотеки».
Далее давайте рассмотрим и настроим структуру проекта более подробно: нажмите
Далее давайте добавим исходный корень, чтобы фактически сделать всю работу. На той же странице «Структура проекта» щелкните правой кнопкой мыши корневой каталог проекта и выберите «Новая папка» в контекстном меню:
Далее введите имя каталога:
Наконец, давайте пометим этот каталог как исходный корень: выберите каталог src и нажмите

Нажмите кнопку ОК, чтобы применить изменения и закрыть диалоговое окно «Настройки / Настройки».
Обратите внимание, что этот шаг на самом деле не является обязательным. Вам просто нужно создать файл под корнем проекта, и он будет рассматриваться как исходный файл, потому что корень проекта по умолчанию является корнем источника.
Создать класс Python
Выберите каталог src в окне инструментов проекта и нажмите Alt + Insert:
Выберите опцию Python file из всплывающего окна и введите новое имя файла (Solver):
PyCharm создает новый файл Python и открывает его для редактирования:
Изменить исходный код
Давайте посмотрим на файл Python, который мы только что сгенерировали. Заглушка содержит только две строки:
Выберите ключевое слово class и введите имя класса (Solver). PyCharm немедленно сообщает вам о пропавшей двоеточии, а затем ожидает отступ:
Обратите внимание на неправильные полосы в правом желобе. Наведите указатель мыши на полосу ошибок, и PyCharm отобразит всплывающую подсказку с подробными инструкциями. Поскольку PyCharm анализирует ваш код в режиме реального времени, результаты немедленно отображаются в контрольном индикаторе в верхней части правого желоба. Этот индикатор проверки похож на светофор: когда он зеленый, все в порядке, вы можете продолжить свой код, желтый индикатор указывает на некоторые незначительные проблемы, но это не повлияет на компиляцию, но когда индикатор становится красным, это означает, что У вас есть серьезные ошибки.
Давайте продолжим и создадим функцию ‘demo’: когда вы вводите только открывающую фигурную скобку, PyCharm создаст всю конструкцию кода (обязательные параметры ‘self’, закрывающая фигурная скобка и двоеточие) и предоставит соответствующий отступ:
Обратите внимание, что при вводе неиспользуемые символы отображаются серым цветом:
Как только дискриминант рассчитан, он воспроизводится как обычно. Далее обратите внимание на неразрешенную ссылку «Математика». PyCharm выделяет его красной кривой и отображает лампочку красного цвета.
Мы решили импортировать математическую библиотеку. Операторы импорта будут добавлены в файл Solver.py. Затем вычислите корень квадратного уравнения и распечатайте его. Наконец, давайте назовем функцию класса Solver для демонстрации:
Затем нажмите Ctrl + Shift + F10, чтобы запустить скрипт. Консоль появится в «Окно запуска инструмента, В этой консоли вы должны ввести значения a, b и c и ожидать результатов.
Кажется, что некоторый анализ желателен, поэтому давайте удостоверимся, что radius’d не неотрицателен и сообщим об ошибке, когда он отрицателен. Чтобы сделать это, выберите дискриминационный оператор вычисления и нажмите Ctrl + Alt + T (Code → Wrap):
PyCharm создает заглушку структуру «если», которая позволяет вам выполнить задачу заполнения правильного содержимого. Наконец, хорошо повторить весь расчет несколько раз, поэтому давайте снова воспользуемся действием «Окружить с»: выделим весь текст демонстрации функции и окружим его while. Вы получите следующий код:
Далее давайте запустим и отладим этот скрипт.
Запустите приложение
Вы уже запустили скрипт Solver с помощью сочетаний клавиш, поэтому давайте просто напомним, как это делается. PyCharm предлагает несколько способов запуска скрипта, открытого в редакторе.
В любом случае PyCharm откроетсяОкно запуска инструментаИ показывает ввод и вывод приложения:
Запустить / отладить конфигурацию
Каждый скрипт использует специальный файл конфигурации илиВыполнить / отладить выполнение конфигурации, Такой файл конфигурации используется для запуска и отладки приложения, а также для указания имени сценария, рабочего каталога, действий, которые необходимо выполнить перед запуском и т. Д.
Давайте подробнее рассмотрим диалоговое окно «Редактировать конфигурацию». Его левая часть содержит древовидное представление с двумя узлами верхнего уровня: Python и Default:
Нижний узел содержит список конфигураций запуска / отладки по умолчанию. Эти конфигурации запуска / отладки по умолчанию являются безымянными, но каждая новая конфигурация запуска / отладки создается на основе конфигурации по умолчанию и получает имя по вашему выбору.
Верхний узел называется Python и содержит только одну конфигурацию запуска / отладки.решающее устройствоОтображается серым цветом. Что это значит?
Запуск / отладка конфигурации Когда вы только что запустили скрипт Solver,SolverСоздано PyCharmВременный файл конфигурации, Он находится под узлом Python, потому что эта конфигурация запуска / отладки находится вТип питонаизКонфигурация по умолчаниюСоздано на основе.
Вы можете сохранить эту конфигурацию запуска / отладки, чтобы сделать ее постоянной. Конфигурация постоянного запуска / отладки отображается обычным шрифтом. В отличие от временных конфигураций, количество постоянных конфигураций не ограничено.
Давайте использовать ту же конфигурацию временного запуска / отладкиSolverОтладить скрипт Solver.
Отладка приложения
Как вы будете проходить через приложение, изучать информацию о программе, связанную с переменными, мониторингом или потоками, чтобы найти источник исключения? Это помощь процесса отладки.
Чтобы начать отладку, вы должны сначала установитьBreakpoints, Чтобы создать точку останова, просто щелкните левый желоб:
Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на фоне редактора и выберите «Отладка» в контекстном меню:
PyCharm начинает сеанс отладки и отображаетОкно инструмента отладки, Следующие изображения соответствуют макету панелей и вкладок по умолчанию:
“ Окно инструмента отладкиВыделенные панели отображают кадры, переменные и мониторинг, а также консоль, которая отображает всю информацию ввода и вывода. Если вы хотите, чтобы консоль всегда была видна, просто перетащите ее в нужное место:
использованиеКнопки панели инструментов StepШаг через ваше приложение:
Когда вы проходите через приложение, каждая достигнутая точка останова становится синей:
Исследуйте навигацию
Навигация приносит особый энтузиазм в PyCharm. Давайте кратко расскажем о многих навигационных возможностях PyCharm.
реконструкция
Поместите курсор в объявление функции, нажмите Shift + F6 и введите новое имя в диалоговом окне «Переименовать»:
Нажмите «Рефакторинг». Все найденные события появляются в «Найти окно инструментов:
Этот класс можно дополнительно изменить: переместить его в другую папку, изменить сигнатуру функции вычисления, извлечь переменные и т. Д. Все эти операции выполняются с помощью различных рефакторингов. Мы рассмотрим эти рефакторинги более подробно в отдельном руководстве.
резюме
Итак, этот короткий урок окончен. Подведем итоги наших достижений:
Интеллектуальная рекомендация
139. Разрыв слов
«SpringSecurityOauth2» 4. Учетные данные клиента grant_type = client_credential
1. Обменяйте сертификат клиента на токен доступа. Приложению необходимо подать заявку на токен доступа от сервера аутентификации, а запрос требует сертификат клиента для аутентификации. Предпол.
java Map
Map спрос: * Сохранить идентификатор студента, имя студента * 2 значения атрибута этого учащегося должны сохраняться каждый раз * s1001 Zhang San Mapping Relations K (KEY) key V (VALUE) value (пара &q.
Советы для общих техник UliPad
UliPadСоветы для общих навыков PythonЯ научился этому некоторое время, и у меня есть под рукойIDEИнструменты также необходимы для написания программ. Я обнаружил, что многие люди используютsublime, Им.
Решите проблему, заключающуюся в том, что нулевое значение в объекте From в BeanUtils и PropertyUtils будет перезаписывать ненулевое значение в объекте To и повысить эффективность и производительность копирования. Как эффективно реализовать метод копирования свойств объекта?
Решите проблему, заключающуюся в том, что нулевое значение в объекте From в BeanUtils и PropertyUtils будет перезаписывать ненулевое значение в объекте To и повысить эффективность и производительность.
Источники информации:
- http://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/creating-and-running-your-first-python-project.html
- http://www.rbsoft.ru/kb/ide-pycharm-windows/
- http://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/generating-a-project-from-a-framework.html
- http://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/creating-and-running-your-first-django-project.html
- http://medium.com/cluj-school-of-ai/getting-started-with-pycharm-d9f58467017
- http://is42-2018.susu.ru/blog/2019/03/01/byil-zadan-vopros-chto-takoe-pycharm/
- http://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/creating-flask-project.html
- http://www.internet-technologies.ru/articles/sozdanie-per-veb-prilozheniya-s-pomoschyu-django.html
- http://russianblogs.com/article/3312159564/